Moles And How To Deal With Them
Your skin is the body organ that covers the largest surface area among body organs. This makes it prone to many different bacteria and viruses that result in various illnesses and conditions. Among the most common skin-related infections include Chevy Chase moles/nevi. This condition is quite prevalent and well-known. More about the disease and suitable treatment plans are discussed below.
Table of Contents
What are moles?
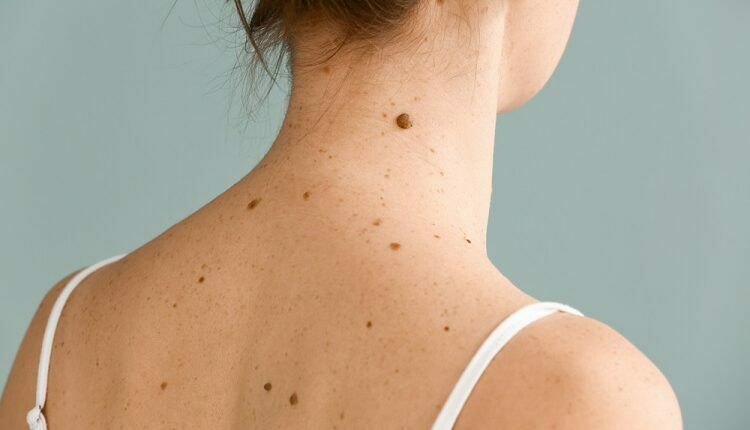
Moles are typical growths of the skin that occur as tiny, dark brown spots resulting from groups of pigment-forming cells. Most people have more than ten moles that come and go during childhood and adolescence while fading over time or changing in appearance.
Most of them are harmless and hardly become cancerous. However, keen observation of mole and other pigmented patches changes is vital in identifying skin cancer such as malignant melanoma.
Signs and Symptoms
A mole usually looks like a tiny brown spot. They can, however, come in various shapes, colors, and sizes:
- Shape – Most moles are shaped round or oval
- Texture and color – Moles can be tan, brown, blue, black, pink, or red. They can be wrinkled, smooth, raised, or flat. Some hair may be growing from them.
- Size – Most mole’s size is typically the size of a pencil eraser. Those born with maybe more prominent moles than usual cover a part of the torso, face, or limb.
Moles may appear on various body parts such as the armpits, scalp, between your toes and fingers, or under your nails. Most moles develop before you become fifty. Adolescent hormonal changes and those found in pregnancy become larger and darker.
Flesh moles are groups of brown spots around the cheeks, eyes, and nose, but they may also be dermatosis papulosa nigra, not pigment-forming cells. These are common in black women and have no risk for melanoma with cosmetic treatments.
Moles with asymmetrical shapes, irregular borders, or changes in shape, color, height, or size may be signs of skin cancer.
Moles come about when skin cells referred to as melanocytes grow together in groups. They are typically distributed all over the skin and produce the substance that gives skin its color, melanin.
Complications when getting moles involve the contraction of melanoma. Factors that may heighten the likelihood of getting melanoma are such as:
- Having unusual moles of irregular shape and size
- Being born with large moles
- Having a family history of melanoma
- Having many moles
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis may be achieved through observation, although a skin exam may be done. This exam is done through skin inspection from head to toe. A suspected cancerous mole has a sample taken and sent to the lab for further scrutiny via a biopsy.
Most moles do not require treatment. Makeup may be applied to conceal it, while a hair growing from it may be clipped. Suspicious changes in your mole may require discussion with your dermatologist. The removal of a mole is quick and done as an outpatient procedure.
Most moles are usually left unattended as they cause no significant harm. But for aesthetic reasons or if the mole is suspected to be cancerous, further analysis for treatment is required. For any mole concerns, visit our website, or call our offices in Chevy Chase, MD.